Introduction:
Parkinson’s disease affects the nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine. Parkinson’s disease symptoms include muscle rigidity, tremors, and changes in speech and gait. After diagnosis, treatments can help decrease symptoms, but there is no cure. This disease is all about an illness that affects the part of your brain that controls how you move your body. It’ll come so gradually that you’ll not even notice it at first, but eventually, it will start as a little shakiness in your hand can have an impact on how you walk, talk, sleep, and think. You’re more likely to get it when you’re 60 or older. It’s also possible for it to start when you’re younger, but that doesn’t happen early as often.
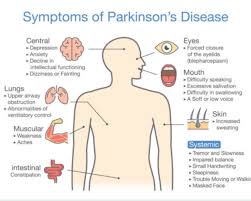
Which other systems could be affected?
This disease affects the Nervous system as Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive disorder that affects nerve cells in the brain responsible for body movement. When dopamine-producing neurons die, symptoms such as tremor, slowness, stiffness, and balance problems occur. Treatments focus on reducing symptoms to enable a more active lifestyle and include medication, diet, exercise, and deep brain stimulation surgery.

What techniques can be used to diagnose the disease? How can transplantation or any other scientific advances play an important role in the treatment of the disease?
No specific test exists to diagnose Parkinson’s disease. Your doctor trained in nervous system conditions (neurologist) will diagnose Parkinson’s disease based on your medical history, a review of your signs and symptoms, and a neurological and physical examination.
Imaging tests such as MRI, CT, ultrasound of the brain, and PET scans may also be used to help rule out other disorders. Imaging tests aren’t particularly helpful for diagnosing Parkinson’s disease.
Parkinson’s disease can’t be cured, but medications can help control your symptoms, often dramatically. In some later cases, surgery may be advised.
There are some medications to it such as:-
Carbidopa-levodopa
Carbidopa-levodopa infusion
Dopamine agonists
MAO B inhibitors
Catechol O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitors
Anticholinergics
Amantadine
The implications of using transplantation or any other scientific advances to cure the disease:
Emotional:
The emotional and psychological impact of Parkinson’s on the patient, family, and caregiver, is profound. It’s hard to fight this kind of disease and you might think of giving up. Thus there is no cure for it but medications and therapies are there to help.
Economical:
Patients with Parkinson’s disease(PD) experience progressive disability and reduced quality of life. The cost of illness increases as PD progresses, placing an economic burden on the healthcare system, society, and patients themselves. Overall cost estimates vary from country to country, but the largest component of direct cost is typically in patient care and nursing home costs, while prescription drugs are the smallest contributor. The total cost in the UK has been estimated to be between pound 449 million and 3.3 billion pounds annually.
Social:
Socially these advances do not hurt the surrounding or the community near the person. Below the age of 40 to 50, it is a rare disease yet it is found more common above the age of 60 years.
By – Talha Jariwala