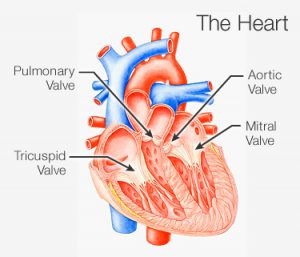
| Your heart valves are located at the exit of each of your four heart chambers (ie. right atrium, left atrium, pulmonary artery and aorta) and maintain one-way blood flow through your heart.In simpler words, the four heart valves act as door guards making sure that blood always flows freely in a forward direction and that there is no backward leakage.
You have four valves in your heart,
Heart valve disease occurs when the heart valves do not work the way described above.There are several types of Heart valve diseases but the most common include :
Diagnosis of this disease could also mean that there is family history of early-onset heart disease and probably the members in your family are very likely to have heart related diseases.Also people with certain autoimmune disorders including lupus, rheumatoid arthritis which both are very likely to be hereditary, are prone to have this disease so looking back into your family’s medical history might give you the reason behind someone in your family having Heart valve disease.Other causes of Heart valve disease include, being present at birth (congenital) or it can also occur in adults due to many causes and conditions, such as infections and other heart conditions. The symptoms of Heart valve disease include :
If you show any of this symptoms then after the doctor’s consultation performing an Echocardiography (echo) is the main test for diagnosing heart valve disease. But an EKG (electrocardiogram) or chest x-ray is commonly used to reveal certain signs of the condition. If these signs are present, echo usually is done to confirm the diagnosis. Heart Valve disease blocks or slows down the blood and oxygen supply you heart normally gives which could be life threatening as organs like brain need oxygen to function without which they start to fail or hemorrhage so the effect of this disease is there on every organ requiring blood which is basically all the organs in your entire freaking body!! Treatment for this diseases include many course of action depending upon which valve needs the treatment and how narrow or completely blocked it is. When treatment for heart valve disease includes surgery, it can be traditional or a minimally invasive procedure known as balloon valvuloplasty where in the widening of a stenotic aortic valve takes place using a balloon catheter inside the valve. The balloon is placed into the aortic valve that has become stiff from calcium buildup.Other common treatment plans include:
When a valve fails to close properly or open properly,the heart has to work harder to pump enough blood to the body, eventually leading to heart muscle damage. If not diagnosed and treated timely than heart transplant is likely to be required as the heart muscle is not strong enough to bear the pumping load. The impacts of this surgery are to a great extent in different factors such as economic. A standard valve replacement can cost $80,000-$200,000 according to an American Heart Association report, to which additional post operation, doctor fee and surgeon fee and the tests and scans fee are added to the bill which are approximately $169,238. On the other hand, such surgeries are what boosting the economy of many cities and giving them worldwide recognition like University of Washington Medical Center (Seattle) and Mayo Clinic Hospital (Phoenix). Another implication of this procedure is the social benefits and barriers it has like it increase the life expectancy of all the patients whose surgery was successful but at the same time the post-op measures are very severe like restriction to work for a long period of time, strict and rigorous bed-rest and a long recovery period if complications had arrived during the surgery. Also another implication includes the ethnic ones where they restrict human organ transplant by stating the the god has planned their future and has gifted them with this body and thus no changes should be made in it. One apt example of this are the Jehovah’s Witness who strictly restrict blood being injected in their body’s no matter how threatening the disease is. On the bright side, Islamic ethnic groups have released Fatwas of their religious leaders clearly stating that human life should be preserved no matter what and that the new organs are like a blessing of Allah to them as a symbol of new life. In summary, Valvular Disease in the heart is caused by a number of conditions including congenital defects, such as rheumatic fever, or rheumatic heart disease. In heart valve disease, problems arise when a valve fails to close properly (mitral valve prolapse) or open properly (valvular stenosis). In either case, the heart has to work harder to pump enough blood to the body, eventually leading to heart muscle damage. Congestive heart failure, syncope (fainting), and arrhythmia are common signs of valve disease. |