What is leukemia? leukemia is also known as blood cancer Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. Leukemia begins in a cell in the bone marrow. The cell undergoes a change and becomes a type of leukemia cell. The leukemia cell has a better life than normal blood cells and they can grow better than the red blood cells. And it usually facts the white blood cells. There are 3 types of leukemias present Chronic and acute leukemia, Lymphocytic and myelogenous leukemia, Acute lymphocytic leukemia.
Some factors increase the risk of developing leukemia. The following are either known or suspected factors:
- artificial ionizing radiation
- viruses, such as the human T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV-1) and HIV
- benzene and some petrochemicals
- alkylating chemotherapy agents used in previous cancers
- hair dyes
Smoking
The symptoms of the diseases are
- Poor blood clotting
- Frequent infections
- Anemia
- Weight loss
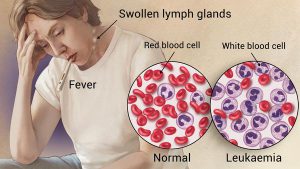
- Fever
What techniques are used to diagnose the disease
First, the doctor will carry out a family medical history. Then the doctors will check for signs of anemia and feel for an enlarged liver or spleen.
The doctors will conduct a normal blood test and if the doctors suspect leukemia they may suggest a bone marrow test. Bone marrow is taken, usually from the hip, using a long, fine needle. This can help to show which kind of leukemia, if any, is present.
Leukemia begins in the soft inner parts of the bone (bone marrow) and quickly spreads into other parts like the spleen, liver, Central nervous system and causes the liver and the spleen to enlarge. Causing fever, weight loss and etc.
The treatments to cure leukemia
There are various types of leukemia, and they affect people differently. Treatment options will depend on the type of leukemia and the person’s age and the overall state of health.
In 1975, the chances of surviving for 5 years or more after receiving a diagnosis of leukemia were 33.1 percent. By 2009, this figure had risen to 62.9 percent.
The treatments include
- targeted therapy
- interferon therapy
- chemotherapy
- radiation therapy
- surgery
- stem cell transplantationChemotherapy can affect the whole body, but targeted therapy is aimed at a specific part of the cancer cell.
Some types of chronic leukemia do not need treatment in the early stages, but monitoring is essential. The oncologist may suggest watchful waiting with frequent doctor’s visits.
For a type of leukemia known as chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), a bone marrow transplant may be effective. Younger patients are more likely to undergo transplantation successfully.
The economic factors
The transplantation is very expensive and the surgeries to are expensive so everybody cannot afford to have a transplant or a surgery done
The cultural factors
As in many religions it specifically in Islam it is not allowed to take a body part out of a person the person should be buried with all the body parts.